Biotech7005
Week 4 Practicals
More Command Line Tips & Tricks
Setup the directory for today
Just as we’ve created a new R Project for practicals 1 to 3, let’s create a new one for today to make sure we’re all in the same place.
- Using the
Filemenu at the top left, selectNew Project - Select
New Directory - Select
New Project - If you’re not already asked to create this project as a subdirectory of
~, navigate to the Home directory using the Browse button - In the
Directory Namespace, enterPractical_4, then hit the Create Project button.
This again helps us keep our code organised and is good practice.
Standard Output
All of the output we saw in the previous practical was ‘printed’ to your terminal.
Each function returned output to you using a data stream called standard out, or stdout for short.
Most of these tools also send information to another data stream called standard error (or stderr), and this is where many error messages go.
This is actually sent to your terminal as well, and you may have seen this if you’ve made any mistakes so far.
This basic data flow can be visualised in the following chart from www.linuxunit.com.
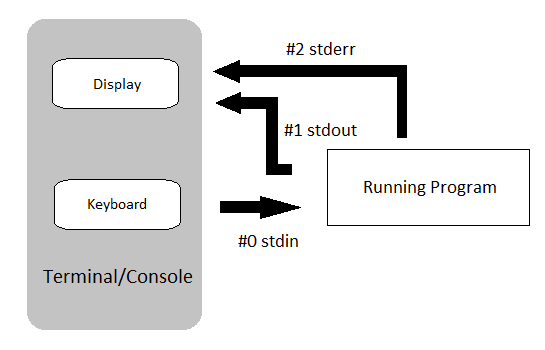
Note also that everything you’ve typed on your keyboard is sent to each command as a data stream called stdin.
Any guesses what that is short for?
Text In the Terminal
We can display a line of text in stdout by using the command echo.
The most simple function that people learn to write in most languages is called Hello World and we’ll do the same thing today.
echo 'Hello World'
That’s pretty amazing isn’t it & you can make the terminal window say anything you want without meaning it.
echo 'This computer will self destruct in 10 seconds!'
There are a few subtleties about text which are worth noting.
If you have man pages accessible, inspect the man echo page & note the effects of the -e option. (Unfortunately you can’t access this using echo --help.)
The -e option allows you to specify tabs (\t), new lines (\n) & other special characters by using the backslash to signify these characters.
This is an important concept & the use of a backslash to escape the normal meaning of a character is very common, as we saw with grep last time.
Try the following three commands & see what effects these special characters have.
echo 'Hello\tWorld'
echo -e 'Hello\tWorld'
echo -e 'Hello\nWorld'
As we’ve seen above, the command echo just repeats any subsequent text.
Now enter
echo ~
Why did this happen?
Sending Output To A File
Using the > symbol
So far, the only output we have seen has been in the terminal (stdout).
Similar to the magrittr in R, we can redirect the output of a command to a file instead of to standard output, and we do this using the greater than symbol (>), which we can almost envisage as an arrow.
As a simple example we can write text to a file.
Using the command echo prints text to stdout
echo "Hello there"
However, we can ‘capture’ this text and redirect it to a file using the > symbol.
echo "Hello there" > hello.txt
Notice that the text no longer appeared in your terminal!
This is because we sent it to the file hello.txt.
To look at the contents of hello.txt use either one of the commands less, cat or head.
Once you’ve looked at it, delete it using the command rm to make sure you keep your folder nice & tidy, as well as free from unimportant files.
Let’s get a more serious file to work with for today.
Make sure you are in your Practical_4 directory, then download the following file using curl
curl ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-89/fasta/drosophila_melanogaster/ncrna/Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa.gz > Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa.gz
If we hadn’t placed this symbol at the end of this command, curl would literally stream all of the contents of this file to stdout, but now we have redirected this to a file!
After you’ve downloaded this file, unzip it using gunzip.
Inspect the contents of the extracted file using head.
head Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
This file is all the ncrna sequences from the current build of D. melanogaster in fasta format.
As you can see, each sequence has a header row which begins with > so if we wanted to just collect the sequence headers we could use egrep and write the output to a file.
egrep '^>' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
This will just dump the information to stdout, and will appear as a stream of identifiers.
If we want to capture stdout and send it to a file, we can use the > symbol again at the end of the above command, and provide a filename to write to.
This will create the file as an empty file, then add the data stream from stdout to the blank file.
egrep '^>' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa > SeqIDs.txt
less SeqIDs.txt
Once you’ve had a quick look at the file, exit the less pager (q) and delete the file using the rm command.
Using the >> symbol
Another alternative is to use the >> symbol, which only creates a blank file if one doesn’t exist.
If one with that name already exists, this symbol doesn’t create an empty file first, but instead adds the data from stdout to the end of the existing data within that file.
echo -e '# Sequence identifiers for all ncrna in dm6' > SeqIDs.txt
In this command, we’ve created a header for the file, and we can now add the information we need after this using the >> symbol.
This trick of writing a header at the start of a file is very common and can be used to add important information to a file.
Now let’s add another row describing where we’ve obtained the data from.
echo -e '# Obtained from ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-89/fasta/drosophila_melanogaster/ncrna/Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa.gz on 2017-08-14' >> SeqIDs.txt
Have a look at the file using less
less SeqIDs.txt
Now we can add the sequence identifiers
egrep '^>' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa >> SeqIDs.txt
Inspect this once again using less, head or cat
Redirection Using The Pipe Symbol
Sometimes we need to build up our series of commands & send the results of one to another.
The pipe symbol (|) is the way we do this & it can literally be taken as placing the output from one command into a pipe & redirecting it somewhere new.
This is where thinking about the output of a command as a data stream can be very helpful.
This is a very conventional approach when working in bash and was the motivation behind the creation of the magrittr package in R.
As a simple example, we could take the output from an ls command & send it to the pager less.
ls -lh /usr/bin | less
Page through the output until you get bored, then hit q to quit.
This process can also be visualised using the following diagram from Unix Bootcamp:
Inspecting genomic files using bash`
As you may have realised, these file types don’t play well with MS Word, Excel and the like.
We need different ways to look through these and as we go, hopefully you’ll get the hang of this.
First we’ll download the file GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff for Lactobacillus amylovorus from the NCBI database. (Use curl if you don’t have wget)
wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/000/182/855/GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1/GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff.gz
gunzip GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff.gz
This file is in gff format, which is very commonly used.
The first 5 lines of this file is what we refer to as a header, which contains important information about how the file was generated in a standardised format.
Many file formats have these structures at the beginning, but for our purposes today we don’t need to use any of this information so we can move on.
Have a look at the beginning of the file just to see what it looks like.
head -n12 GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff
Notice the header lines begin with one or two hash symbols, whilst the remainder of the file contains information about the genomic features in tab-separated format. As there is a lot of information about each feature, note that each line after the header will probably wrap onto a second line in the terminal. The first feature is annotated as a region in the third field, whilst the second feature is annotated as a gene.
Question
- How many features are contained in this file?
- If we tried the following:
wc -l GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gffwould it be correct?
This will give 4446, but we know the first 5 lines are header lines. To count the non-header lines you could try several things:
grep -vc '^#' GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff
or
grep -c '^[^#]' GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff
Make sure you understand both of the above commands as it may not be immediately obvious!
As mentioned above, this file contains multiple features such as regions, genes, CDSs, exons or tRNAs. If we wanted to find how many regions are annotated in this file we could use the processes we’ve learned above:
grep -c 'region' GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff
If we wanted to count how many genes are annotated, the first idea we might have would be to do something similar using a search for the pattern 'gene'.
Question
Do you think this is the number of regions & genes?
- Try using the above commands without the
-cto inspect the results. - Try searching for the number of coding DNA sequences using the same approach (i.e. CDS) & then add the two numbers?
- Is this more than the total number of features we found earlier?
- Can you think of a way around this using regular expressions?
Some of the occurrences of the word gene or region appear in lines which are not genes or regions. We could restrict the search to one of the tab-separated fields by including a white-space character in the search. The command:
egrep '\sgene\s' GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff | wc -l
will give a different result again as now we are searching for the word gene surrounded by white-space.
Note that we’ve also used the pipe here to count results using the wc command.
We could have also used egrep with the -c flag set.
Using cut
Alternatively, there is a command cut available.
Call the manual page (man cut) and inspect the option -f.
man cut
We can simply extract the 3rd field of this tab-delimited file by using the f3 option.
cut -f3 GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff | head -n12
(You can ignore any errors about a Broken pipe.)
However, this hasn’t cut the third field from the header rows as they are not tab-delimited.
To remove these we need to add one further option.
Call up the man page and look at the -s option.
This might seem a bit confusing, but this means don’t print lines without delimiters which would be the comment lines in this file.
cut -f3 -s GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff | head
Now we could use our egrep approach and we know we’re counting the correct field.
cut -f3 -s GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff | egrep -c 'gene'
A similar question would be: How many types of features are in this file?
The commands cut, along with sort and uniq may prove to be useful when answering this
cut -f3 -s GCF_000182855.2_ASM18285v1_genomic.gff | sort | uniq -c
In the above some of the advantages of the pipe symbol can clearly be seen. Note that we haven’t edited the file on disk, we’ve just streamed the data contained in the file into various commands.
sed: The Stream Editor
One additional and very useful command in the terminal is sed, which is short for stream editor.
Instead of the man page for sed the info sed page is larger but a little easier to digest.
This is a very powerful command which can be a little overwhelming at first.
If using this for your own scripts & you can’t figure something out, remember ‘Google is your friend’ & sites like \url{www.stackoverflow.com} are full of people wrestling with similar problems to you.
These are great places to start looking for help & even advanced programmers use these tools.
For today, there are two key sed functionalities that we want to introduce.
- Using
sedto alter the contents of a file/input; - Using
sedto print regions of a file
Altering a file or other input
sed uses regular expressions that we have come across under the grep section, and we can use these to replace strings or characters within a text string, like we did in R using str_extract() and str_replace().
The command works in the form sed 'SCRIPT' INPUT, and the script section is where all the action happens.
Input can be given to sed as either a file, or just as a text stream via the pipe that we have already introduced.
In the following example the script begins with an s to indicate that we are going to make a substitution.
The beginning of the first pattern (i.e. the regexp we are searching for) is denoted with the backslash, with the identical delimiter indicating the replacement pattern, and this is in turn completed with the same delimiter.
Try this simple example from the link \url{http://www.grymoire.com/Unix/Sed.html} which is a very detailed & helpful resource about the usage sed.
Here we are sending the input (echo Sunday) to the command via the pipe, so no INPUT section is required:
echo Sunday | sed 's/day/night/'
Here you are passing sed the string Sunday, and sed takes day and turns it into night.
sed will only replace the first instance of the string on any line, so try:
echo Sundayday | sed 's/day/night/'
It only replaced the first instance of day and left the second. You can make it ‘global’, where it switches every instance by using the g option at the end of the pattern like this:
echo Sundayday | sed 's/day/night/g'
You can ‘capture’ parts of the pattern in parentheses and access that in the second part of the regular expression (what you are switching to) using \1, \2, etc., to denoted the number of the captured string.
If you wanted to match ATGNNNTGA, where N is any base, and just output these three bases you could try the following
echo 'ATGCCAGTA' | sed -r 's/ATG(.{3})GTA/\1/g'
Or if we needed to replace those three bases with an expanded tri-nucleotide repeat of them, you could do the following where we capture the undefined string between ATG & GTA, and expand it to three times:
echo 'ATGCCAGTA' | sed -r 's/ATG(.{3})GTA/ATG\1\1\1GTA/g'
The \1 entry takes the contents of the first parenthesis and uses it in the substitution, even though you don’t know what the bases are.
Note that the -r option was set for these operations, which turns on extended regular expression capabilities.
This can be a powerful tool & multiple parentheses can also be used:
echo 'ATGCCAGTA' | sed -r 's/(ATG)(.{3})(GTA)/\3\2\2\1/g'
In this command we captured each codon separately, then switched the order of the first & last triplet and expanded the middle unknown string twice. Note how quickly this starts to look confusing though! Taking care to be clear when writing these types of procedures can be an important idea when you have to go back & re-read your code a year or two later. (Yes this will happen a lot!!!)
Displaying a region from a file
The command sed can also be used to replicate the functionality of the head & grep commands, but with a little more power at your fingertips.
By default sed will print the entire input stream it receives, but setting the option -n will turn this off.
Try this by adding an n immediately after the -r in one of the above lines & you will notice you receive no output.
This is useful if we wish to restrict our output to a subset of lines within a file, and by including a p at the end of the script section, only the section matching the results of the script will be printed.
Make sure you are in the Practical_4 directory & we can look through the file Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa again.
sed -n '1,10 p' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
This will print the first 10 lines, like the head command will by default.
However, we could now print any range of lines we choose.
Try this by changing the script to something interesting like 101,112 p.
We could also restrict the range to specific lines by using the sed increment operator ~.
sed -n '1~4p' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
This will print every 4th line, beginning at the first, and is very useful for files with multi-line entries.
The fastq file format from NGS data, and which we’ll look at in week 6 will use this format.
We can also make sed operate like grep by making it only print the lines which match a pattern.
sed -rn '/TGCAGGCTC.+(GA){2}.+/ p' Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
Note however, that the line numbers are not present in this output, and the pattern highlighting from grep is not present either.
Writing Scripts
Now we’ve had a look at many of the key tools, we’ll move on to writing scripts which is one of the most common things a bioinformatician will do. We often do this on a HPC to run long data processing pipelines (or workflows).
Scripts are commonly written to perform repetitive tasks on multiple files, or need to perform complex series of tasks and writing the set of instructions as a script is a very powerful way of performing these tasks. They are also an excellent way of ensuring the commands you have used in your research are retained for future reference. Keeping copies of all electronic processes to ensure reproducibility is a very important component of any research. Writing scripts requires an understanding of several key concepts which form the foundation of much computer programming, so let’s walk our way through a few of them.
Some Important Concepts
Two of the most widely used techniques in programming are that of the for loop, and logical tests using an if statement.
for Loops
A for loop is what we use to cycle through an input one item at a time
for i in 1 2 3; do (echo "$i^2 = $(($i*$i))"); done
In the above code the fragment before the semi-colon asked the program to cycle through the values 1, 2 & 3, letting the variable i take each value in order of appearance.
- Firstly: i = 1, then i = 2 & finally i = 3.
- After that was the instruction on what to do for each value where we multiplied it by itself
$(($i*$i)) to give $i^2$. We placed this as the text string (“$i^2 = $(($i*$i))”) for anecho` command to return.
Note that the value of the variable i was prefaced by the dollar sign ($).
This is how the bash shell knows it is a variable, not the letter i.
The command done then finished the do command.
All commands like do, if or case have completing statements, which respectively are done, fi & esac.
An important concept which was glossed over in the previous paragraph is that of a variable.
These are essentially just placeholders which have a value that can change, much like an object in R.
In the above loop, the same operation was performed on the variable i, but the value changed from 1 to 2 to 3.
Variables in shell scripts can hold numbers or text strings and don’t have to be formally defined as in some other languages.
We will commonly use this technique to list files in a directory, then to loop through a series of operations on each file.
If Statements
If statements are those which only have a binary yes' or no’ response.
For example, we could specify things like:
- if (
i>1) thendosomething, or - if (
fileName == bob.txt) thendosomething else
Notice that in the second if statement, there was a double equals sign (==).
This is the programmers way of saying compare the first argument with the second argument.
A single equals sign is generally interpreted by a program as assign the first argument to be what is given in the second argument.
This use of double operators is very common, notably you will see && to represent the command and, and || to represent or.
A final useful trick to be aware of is the use of an exclamation mark to reverse a command.
A good example of this is the use of the command != as the representation of not equal to in a logical test.
Shell Scripts
Now that we’ve been through just some of the concepts & tools we can use when writing scripts, it’s time to tackle one of our own where we can bring it all together.
Every bash shell script begins with what is known as a shebang, which we would commonly recognise as a hash sign followed by an exclamation mark, i.e \#!.
This is immediately followed by /bin/bash, which tells the interpreter to run the command bash in the directory /bin.
This opening sequence is vital & tells the computer how to respond to all of the following commands.
As a string this looks like:
#!/bin/bash
The hash symbol generally functions as a comment character in scripts. Sometimes we can include lines in a script to remind ourselves what we’re trying to do, and we can preface these with the hash to ensure the interpreter doesn’t try to run them. It’s presence as a comment here, followed by the exclamation mark, is specifically looked for by the interpreter but beyond this specific occurrence, comment lines are generally ignored by scripts & programs.
An Example Script
Let’s now look at some simple scripts. These are really just examples of some useful things you can do & may not really be the best scripts from a technical perspective. Hopefully they give you some pointers so you can get going
Don’t try to enter these commands directly in the terminal!!! They are designed to be placed in a script which we will do after we’ve inspected the contents of the script (see next page). First, let’s just have a look through the script & make sure we understand what the script is doing.
#!/bin/bash
# First we'll declare some variables with some text strings
ME='Put your name here'
MESSAGE='This is your first script'
# Now well place these variables into a command to get some output
echo -e "Hello ${ME}\n${MESSAGE}\nWell Done!"
- You may notice some lines that begin with the # character. These are comments which have no impact on the execution of the script, but are written so you can understand what you were thinking when you wrote it. If you look at your code 6 months from now, there is a very strong chance that you won’t recall exactly what you were thinking, so these comments can be a good place just to explain something to the future version of yourself. There is a school of thought which says that you write code primarily for humans to read, not for the computer to understand.
- Another coding style which can be helpful is the enclosing of each variable name in curly braces every time the value is called, e.g.
${ME}Whilst not being strictly required, this can make it easy for you to follow in the future when you’re looking back. - Variables have also been named using strictly upper-case letters. This is another optional coding style, but can also make things clear for you as you look back through your work. Most command line tools use strictly lower-case names, so this is another reason the upper-case variable names can be helpful.
Question
In the above script, there are two variables. Although we have initially set them to be one value, they are still variables. What are their names?
Writing and Executing Our First Script
Let’s create an empty file which will become our script.
We’ll give it the suffix .sh as that is the common convention for bash scripts.
Make sure you’re in the Practical_4 folder, then enter:
touch wellDone.sh
Now open this using the using the text editor nano:
nano wellDone.sh
Enter the above code into this file setting your actual name as the ME variable, and save it by using Ctrl+o (indicated as ^O) in the nano screen.
Once you’re finished, you can exit the nano editor by hitting Ctrl+x (written as ^X).
Assuming that you’ve entered everything correctly, we can now execute this script by simply entering
bash wellDone.sh
Setting File Permissions
Unfortunately, this script cannot be executed without calling bash explicitly but we can also enable execution of the file directly by setting the execute flag in the file permissions.
First let’s look at what permissions we have:
ls -lh *.sh
You should see output similar to this:
-rw-rw-r-- 1 biotech7005 biotech7005 247 Aug 14 14:48 wellDone.sh
- Note how the first entry is a dash (
-) indicating this is a file. - Next come the three Read/Write/Execute triplets which are
rw-followed byrw-andr--
Question
Interpret the final triplet? What are these permissions indicating, and for whom?
As you can see, the x flag has not been set in any of the triplets, so this file is not executable as a script yet.
To do this, we simply need to set the x flag, then we’ll look again using long-listing format.
chmod +x wellDone.sh
ls -lh *.sh
Note how the file now has the x flag set for every user, which means every user can execute this script.
Now we can execute the script by calling it using the file path.
One of the settings in bash though won’t allow you to execute the file from the same folder, so we need to add the ./ prefix to the script.
./wellDone.sh
We can set each of these flags for all triplets using + to turn the flag on, or - to turn the flag off.
If we wanted to remove write permissions for all users we could simply use the command:
chmod -w wellDone.sh
ls -lh *.sh
This can be a very useful trick for write-protecting files!
These flags actually represent binary bits that are either on or off. Reading from right to left:
- the first bit is the execute flag, which has value 1
- the second bit is the write flag, which has the value 2
- the third bit is the read flag, which has the value 4
Thus each combination of flags can be represented by a single integer, as shown in the following table:
| Value | Binary | Flags | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 000 |
--- |
No read, no write, no execute |
| 1 | 001 |
--x |
No read, no write, execute |
| 2 | 010 |
-w- |
No read, write, no execute |
| 3 | 011 |
-wx |
No read, write, execute |
| 4 | 100 |
r-- |
Read, no write, no execute |
| 5 | 101 |
r-x |
Read, no write, execute |
| 6 | 110 |
rw- |
Read, write, no execute |
| 7 | 111 |
rwx |
Read, write, execute |
We can now set permissions using a 3-digit code, where 1) the first digit represents the file owner, 2) the second digit represents the group permissions and 3) the third digit represents all remaining users.
To set the permissions for our script to read-write-executefor you and any other users in the group you belong to, we could now use
chmod 774 wellDone.sh
ls -lh *sh
Question
What will the final 4 in the above settings do?
Modifying our script
In the initial script we used two variables ${ME} and ${MESSAGE}.
Now let’s change the variable ${ME} in the script to read as ME=$1.
First we’ll create a copy of the script to edit, and then we’ll edit using nano
cp wellDone.sh wellDone2.sh
nano wellDone2.sh
We may need to set the execute permissions again.
chmod +x wellDone2.sh
ls -lh *sh
This time we have set the script to receive input from stdin (i.e. the terminal), and we will need to supply a value, which will then be placed in the variable ${ME}.
Choose whichever random name you want (or just use “Boris” as in the example) and enter the following
./wellDone2.sh Boris
As you can imagine, this style of scripting can be useful for iterating over multiple objects. A trivial example, which builds on a now familiar concept would be to try the following.
for n in Boris Fred; do (./wellDone2.sh ${n}); done
As a good example, this script could summarise key features in a file.
Then we could simply pass the script multiple files using this strategy, and write the output to another file using the > symbol.
Using for Loops
Here’s an example of a script which uses a for loop.
#!/bin/bash
FILES=$(ls)
COUNT=0
for f in ${FILES};
do
((COUNT++))
ln=$(wc -l ${f} | sed -r 's/([0-9]*).+/\1/g')
echo "File number ${COUNT} (${f}) has ${ln} lines"
done
Task
Save this as a script in the Practical_4 folder called lineCount.sh.
Add comments where you think you need them to make sure you understand what’s happening.
A More Advanced Script
In this section we’ll write a script for the dm6:ncrna fasta file. Briefly inspect the file before checking the script to remind yourself what it looks like. We’re going to extract some key information from those sequence header lines.
head Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa
Now let’s look through the following script before we run it. There is a lot of extra information here!
#!/bin/bash
INFILE=$1
# Check the file has the suffix .fa or .fasta
SUFFIX=$(echo ${INFILE} | sed -r 's/.+(fasta|fa)$/\1/')
if [ ${SUFFIX} == "fa" ] || [ ${SUFFIX} == "fasta" ]; then
echo File has the suffix ${SUFFIX}
else
echo File does not have the suffix 'fa' or 'fasta'. Exiting with error.
exit 1
fi
# Define the output file by changing the suffix to .locations
OUTFILE=${INFILE%.${SUFFIX}}.locations
echo Output will be written to $OUTFILE
# Get the header lines which correspond to chromosomes, then collect the
# gene id, chromosome, start and end and write to the output file
egrep '^>.+chromosome' ${INFILE} | \
sed -r 's/.+BDGP6:([^:]*):([0-9]+):([0-9]+).+gene:([^ ]+).+/\4\t\1\t\2\t\3/g' \
> ${OUTFILE}
echo Done
- After the
shebang, the first line takes a filename as input. - The next set of lines contains two processes:
- The suffix
fastaorfais pulled from the filename and passed to the variable${SUFFIX}. What will this return if the suffix is not either of these? - Next, the value of the new variable
${SUFFIX}is checked to make sure it contains onlyfaorfasta+ If this condition is met a message will print tostdout+ If one of these conditions is not satisfied, the script will exit giving an error message (exit 1) - The output file (
OUTFILE) is defined by changing the suffix from whichever is provided to.locations. The use of the%to snip the filename and replace with another is a very useful trick- Finally the header lines containing the word “chromosome” are piped into
sedsedthen captures the chromosome ([^:]*), start ([0-9]+), end ([0-9]+) and gene id ([^ ]+)- These are returned in the order gene id, chromosome, start, end
- All information is written to the file specified in
${OUTFILE}`
- Finally the header lines containing the word “chromosome” are piped into
- The suffix
Save this as the file getLocations.sh and make it executable using chmod +x
Now run it passing the .fa file as the first argument.
./getLocations.sh Drosophila_melanogaster.BDGP6.ncrna.fa